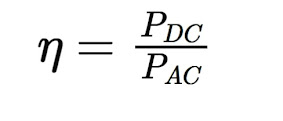Half -Wave Rectifier
Half-Wave Rectifier :
- A Half-Wave Rectifier Is A Simple Electronic Circuit That
Converts Alternating Current (AC) Into Pulsating Direct Current
(DC).
- A Halfwave Rectifier Circuit Uses Only One Diode For The
Transformation.
- It Allows The Positive Half Cycles Of The Input Waveform To
Pass Through While Blocking The Negative Half Cycles.
Circuit :
- A Half-Wave Rectifier Is The Simplest Form Of The Rectifier And
Requires Only One Diode For The Construction Of A Halfwave
Rectifier Circuit.
- A Halfwave Rectifier Circuit Consists Of Three Main Components
As Follows:
(1) Diode
(2) Transformer
(3) Resistive Load
- Diode: The Circuit Consists Of A Diode, Which Is A
Semiconductor Device That Allows Current To Flow In
Only One Direction.
Working Of Half Wave Rectifier Circuit :
- Alternating Current (AC) Input:
The Half-Wave Rectifier Circuit Receives An AC Input Signal,
Typically From A Mains Power
Supply.
- Diode Forward Bias:
During The Positive Half Cycle Of The Input Waveform, The
Voltage At The Anode Of The Diode Becomes Higher Than The
Voltage At The Cathode. This Forward Biases The Diode.
- Diode Conducts:
When The Diode Is Forward-Biased, It Allows Current To Flow
Through It In The Forward Direction.The Diode Acts As A Closed
Switch, Permitting The Passage Of Current.
- Current Flow:
The Forward-Biased Diode Allows The Positive Half Cycles Of
The Input AC Signal To Pass Through It. As A Result, Current
Flows Through The Load Resistor In The Circuit.
- Voltage Developed:
The Current Flowing Through The Load Resistor Creates A
Voltage Drop Across It. This Voltage Drop Represents The
Output Voltage Of The Rectifier Circuit.
- Diode Reverse Bias:
During The Negative Half Cycle Of The Input Waveform, The
Voltage At The Cathode Becomes Higher Than The Voltage At
The Anode. This Reverse Biases The Diode.
- Diode Blocks Current:
When The Diode Is Reverse-Biased, It Does Not Conduct
Current. The Diode Acts As An Open Switch, Preventing The
Flow Of Current.
- No Output Voltage:
Since The Diode Blocks Current Flow During The Negative Half
Cycles, No Voltage Is Developed Across The Load Resistor
During This Period. The Output Voltage Remains At Zero.
- Pulsating DC Output:
The Output Waveform Of A Half-Wave Rectifier Is A Pulsating
DC Waveform. It Consists Of A Series Of Positive Half Cycles
Where The Output Voltage Is Present, Separated By Zero
Voltage During The Negative Half Cycles.
- Ripple Voltage:
The Pulsating DC Output Of A Half-Wave Rectifier Has A
Relatively High Ripple Voltage Due To The Absence Of
Rectification During The Negative Half Cycles. The Ripple
Voltage Represents The Fluctuation Or Variation In The Output
Voltage.
- Smoothing With Capacitor (Optional):
To Reduce The Ripple Voltage And Obtain A Smoother DC
Output, A Filter Capacitor Can Be Connected Across The Load
Resistor. The Capacitor Charges Up During The Positive Half
Cycles, Supplying Current To The Load, And Discharges Slowly
During The Negative Half Cycles, Reducing The Ripple.
Half Wave Rectifier Waveform :
Half Wave Rectifier Formula :
(1) Ripple Factor Of Half Wave Rectifier :
- Ripple Factor Determines How Well A Halfwave Rectifier Can
Convert AC Voltage To DC Voltage.
-
- Ripple Factor Determines How Well A Halfwave Rectifier Can
Convert AC Voltage To DC Voltage.
(2) Efficiency Of Halfwave Rectifier :
- The Efficiency Of A Half-Wave Rectifier Is A Measure Of How
Effectively It Converts The Input AC Power To DC Power.
-
(3) RMS Value Of Half Wave Rectifier :
-
(4) Form Factor Of A Halfwave Rectifier :
- The Form Factor Is Defined As The Ratio Of The RMS Value To
The Average Value Of The Output Waveform
-
Applications Of Half Wave Rectifier :
- They Are Used For Signal Demodulation Purpose
- They Are Used For Rectification Applications
- They Are Used For Signal Peak Applications
Disadvantages Of Half Wave Rectifier :
- Power Loss
- Low Output Voltage
- The Output Contains A Lot Of Ripples
#HalfWaveRectifier
#Rectifier
#ACtoDC
#DiodeRectifier
#Electronics
#PowerConversion
#ElectricalEngineering
#RippleVoltage
#DCPower
#CircuitDesign
#PowerSupply
#ElectronicComponents
#SemiconductorDevices
#Rectification
#PowerElectronics
#ElectricalCircuits
#VoltageConversion
#ElectricalComponents